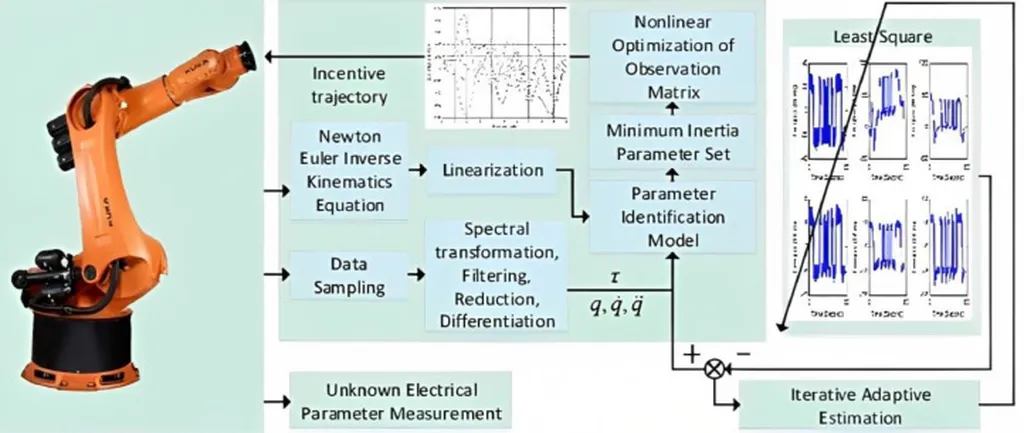
In the realm of industrial robotics, efficiency and precision are paramount. A recent study published in the journal *Mining, Construction, Road and Reclamation Machines* (Гірничі, будівельні, дорожні та меліоративні машини) has taken a significant stride in optimizing the performance of the Niryo One robotic platform. Led by Dmytro Mishchuk from the Kyiv National University of Construction and Architecture, the research focuses on enhancing the manipulator’s drive modes, with promising implications for the energy sector and beyond.
The study, titled “Improvement of the Niryo One Robotic Platform through Optimization of Manipulator Drive Modes. Part II,” delves into the development of a mathematical model that captures the dynamics of the Niryo One manipulator. This model serves as the foundation for optimizing the manipulator’s trajectories using the Sequential Least Squares Programming (SLSQP) method. The goal? To minimize energy consumption and task execution time while adhering to the system’s dynamic constraints.
“Our approach leverages numerical methods of nonlinear programming to determine optimal motion regimes,” explains Mishchuk. “By doing so, we’ve achieved trajectories that reduce the load on the drives and enhance the smoothness of motion compared to the standard modes implemented in the platform’s software.”
The results are compelling. The optimized trajectories not only improve energy efficiency but also enhance the overall dynamics of the manipulator’s operation. This is a significant advancement, particularly for industries where precision and energy efficiency are critical, such as mining, construction, and manufacturing.
The commercial impacts of this research are substantial. In the energy sector, for instance, robotic systems are increasingly deployed for tasks ranging from maintenance to material handling. Optimizing these systems for energy efficiency can lead to significant cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Moreover, the enhanced precision and reliability of these robots can improve safety and productivity in high-risk environments.
Looking ahead, the research opens up new avenues for the development of control algorithms for two-mass robotic systems. “The perspectives for further research involve adapting the developed method for manipulators with different kinematic schemes and under varying external loads,” Mishchuk adds.
As the field of robotics continues to evolve, the insights from this study could pave the way for more advanced and efficient robotic systems. By pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, researchers like Mishchuk are not only shaping the future of industrial robotics but also contributing to a more sustainable and productive energy sector.