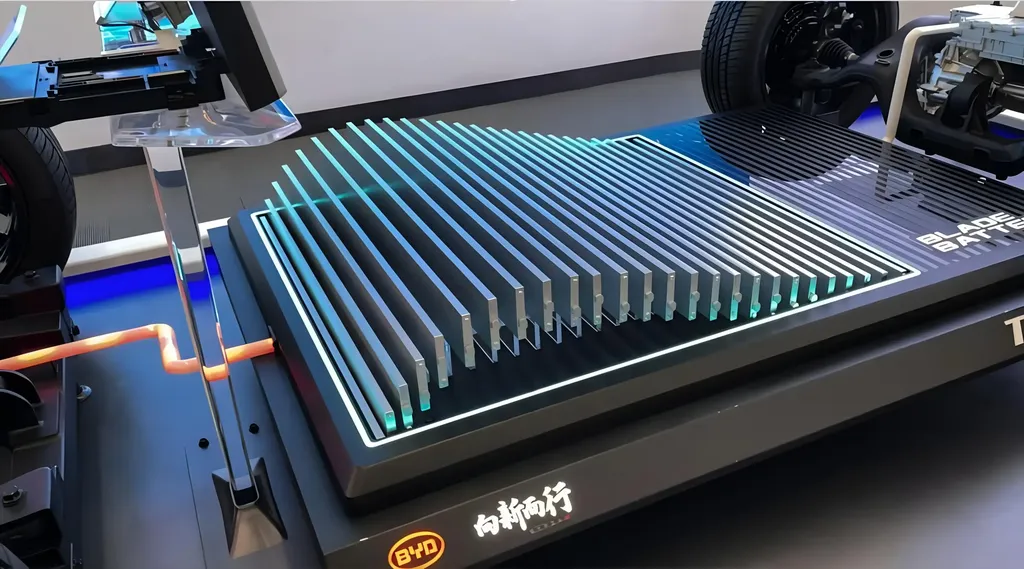
Chinese electric vehicle (EV) manufacturer BYD is making significant strides in battery technology, aiming to reduce the industry’s dependence on critical minerals like cobalt and nickel. The company’s Blade Battery technology is designed to minimize the use of these minerals in EV production, positioning itself as a sustainability enhancement in the global shift toward greener transportation.
The current high and growing demand for cobalt and nickel presents both supply chain challenges and environmental concerns. Exploration companies such as Aston Bay Holdings Ltd. continue to seek viable deposits of these battery metals, confident in the market opportunities within industries supporting the energy transition. This persistent demand underscores the importance of technological alternatives that could alleviate pressure on mineral supply chains.
BYD’s approach represents a strategic response to multiple challenges facing the EV industry. Reducing cobalt and nickel requirements addresses potential supply constraints, ethical concerns surrounding mining practices, and environmental impacts associated with mineral extraction. The Blade Battery technology emerges as the company’s proposed solution to these interconnected issues.
In the broader context, specialized communications platforms like Rocks & Stocks play a crucial role in delivering insights into the mining industry. As part of the Dynamic Brand Portfolio at IBN, such platforms distribute content across numerous outlets while providing corporate communications solutions. Their role in disseminating information about mineral exploration and battery technology developments highlights the interconnected nature of these industries.
For stakeholders monitoring the EV sector, BYD’s technological direction signals a potential shift in battery composition strategies. As the transportation industry continues its transition toward electrification, innovations that reduce reliance on specific minerals could influence manufacturing costs, supply chain stability, and environmental sustainability metrics. The full implications of such technological developments will become clearer as adoption progresses and alternative battery chemistries undergo further testing and implementation in commercial vehicle production.
This news could shape the development of the sector in several ways. Firstly, it may accelerate the adoption of alternative battery technologies that reduce reliance on critical minerals. This could lead to a more sustainable and ethical supply chain, addressing both environmental and social concerns. Secondly, it may prompt exploration companies to diversify their portfolios, investing in minerals that are less likely to face supply constraints or ethical scrutiny. Lastly, it could influence policy decisions, as governments may incentivize the development and adoption of such technologies to meet their climate goals and reduce dependence on volatile mineral markets.
In conclusion, BYD’s Blade Battery technology is a significant development in the EV industry, with potential implications for supply chains, manufacturing costs, and environmental sustainability. As the sector continues to evolve, such innovations will play a crucial role in shaping its future trajectory.